The Basics of SMD Resistors
The resistors used in SMD chips are ubiquitous. Several devices sold on the market each year contain these chips. They include precision laboratory testing equipment, aerospace electronics, handheld devices, and much more. To choose the right SMD resistor for your design, you should be able to read the code on the resistor.
What is an SMD Resistor?
It is a resistor that is designed for surface mounting. It is usually smaller compared to traditional resistors, thereby, taking up just a little space on the circuit board. The acronym, SMD, means Surface Mounted Device. The electronic component is mounted on the circuit board using surface mount technology.
The technology aims to reduce the sizes of components as well as the time consumed when manufacturing circuits. Typically, you only need to handle SMD resistors when manufacturing a PCB professionally. Most DIYers use the “through-hole” type of resistor when building a circuit.
While an SMD resistor may look enticing, if you want to make a homemade circuit, you may need to stick to the through-hole type. This is because SMD resistors are not very easy to assemble and require specialized equipment. But if you are ready to take up the challenge, keep reading and we’ll show you how to get started.
How to Read SMD Resistor Codes
When looking at the resistor, you will observe that it does not have any color band like the through-hole model. This is because the component is so small that there is not enough room to print a color code on it. However, to solve this challenge, there are standardized coding systems. Below are guidelines for using each system.
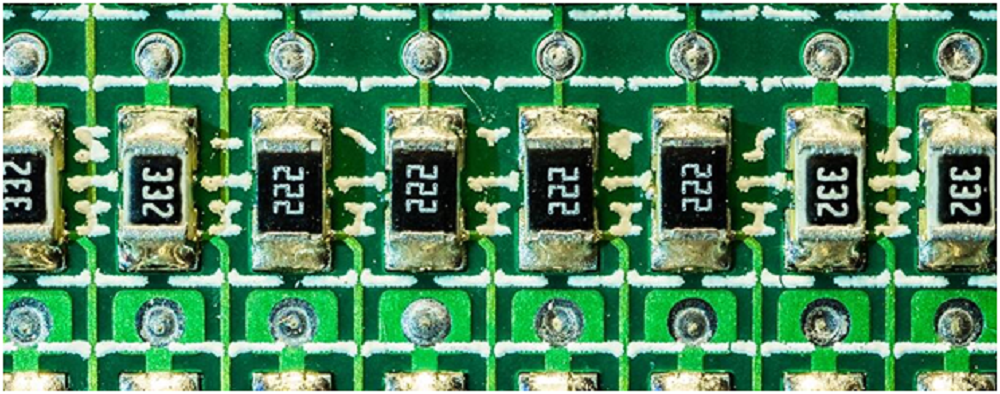
The 3-Digit Coding Technology
This system showcases three digits such that two digits define the resistor’s value. The last digit serves as a multiplier to calculate a resistance value that is higher than ten ohms. When the value is less than ten ohms, the letter, R, defines where you will place a decimal point. When the resistor bears 7R4, for instance, its resistance is 7.4 ohms.
Unlike the color-coding system, the 3-digit coding multiplier indicates 10 raised to the power of the last number. For instance, a resistor bearing 282 would be 28 x 102. We will show you a few examples that will help you understand the 3-digit coding technology better. You can also visit https://pimylifeup.com/resistor-color-code/ to get a color code guide to calculating resistance.
Example 1
Assuming the component is numbered 802, we will regard the first 2 numbers as the base value. Therefore, our base value is 80. Next, we will multiply it by ten raised to the power of 2 (the last digit). From here, we can calculate the resistance, which is 80 x 102 = 8000 ohms or 8k ohms.
Example 2
Assuming the component bears 5R3, there is no need for a multiplier. What you should do is to pick the first digit, place a decimal point in the R position, then the last digit comes next. Therefore, the resistance is 5.3 ohms.
Example 3
Assuming the component bears R34, you can see that the R comes before the digits. Hence, the decimal point will appear before the digits. Considering this, the resistance will be 0.35 ohms.
The 4-Digit Coding Technology
This is quite similar to the 3-digit coding technology. The difference is the addition of an extra digit. Here, the first 3 digits represent the base value of the resistance while the last digit serves as the multiplier’s power. Let’s see a few examples.
Example 1
Assuming the resistor is a 4411 component. The first step is to write down the first 3 digits. This means that the base value is 441 ohms. Subsequently, the last number, 1, becomes the multiplier. Therefore, the resistance will be 441 x 101 = 4410 ohms.
Example 2
Assuming the component bears 67R31. As we already know, the R stands as a decimal point, so we do not need a multiplier. Therefore, the resistance is 67.31 ohms.
Factors Affecting SMD Resistors
Generally, resistors have a high rate of malfunction than other components. This rate is influenced by high pressure and high temperature. Therefore, in certain situations, there is a need to carefully estimate the resistor’s life. To do this, you should consider the following:
1. If the external force is more than a certain limit, the resistance may break.
2. An extremely high temperature can damage the resistor.
3. The surrounding’s level of acidity and alkalinity can rust the resistance, causing harm to the device and the environment.
In order to overcome these problems, doing the following can help to extend the resistor’s life:
1. Maintaining a good power dissipation.
2. Avoiding external forces.
3. Ensuring that the surroundings are toxin-free.
4. Maintaining a dry surrounding to prevent fast burnout.
A resistor that has a high resistance will have a long life. You can visit this website to read about the specifications for SMD resistors.
The Pros and Cons of SMD Resistors
The advantages include the following:
1. Small size
2. A high density of the component
3. Easy and quick to assemble
4. Little errors are easy to trace and correct
5. Tolerance and accuracy
6. Good mechanical performance
7. Reduced inductance
8. Cost-effective
The disadvantages are as follows:
1. The component is highly sensitive
2. Small volume and power
3. The surface mounted technology does not apply to large, high-voltage, high-power parts such as a power circuitry
4. Component repair could prove difficult
Conclusion
SMD (surface mounted device) resistors are widely manufactured and utilized in almost all electronic circuits. They are not difficult to manufacture and you can obtain them at a cheaper rate if you are buying a large quantity. The resistor uses surface mount technology and its main benefits are ease of assembly, small size, and high transmission speed.
Surface mount technology helps to automate production, reduce the cost of materials, and improve efficiency. However, it is not void of lapses, such as high sensitivity. But this should not deter you because the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
- 7 Key Web Design Principles To Create Impactful Web Experiences - June 20, 2024
- Why Your Small Business Needs SEO To Succeed - June 1, 2024
- Ultimate Guide to How Encoders Work: Types & Applications - June 1, 2024